- 首页
- » 搜索
- » joeydeng 发表的帖子
页次: 1
#1 Re: 全志 SOC » F1C100S 卡在 Starting kernel ... » 2024-09-02 18:39:06
btw 3m并不是绝对的判断方法,我是通过判断vmlinux的大小
root@:/linux-nand# ls -lh vmlinux
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 11M Sep 2 10:10 vmlinux
root@:/linux-nand#linux-nand# ll -h arch/arm/boot/zImage
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2.9M Sep 2 10:10 arch/arm/boot/zImage*
root@:/linux-nand#linux-nand#
vmlinux是解压后的kernel大小,如果这个基本占满了整个内存大小,那么就会启动不起来
#2 Re: 全志 SOC » F1C100S 卡在 Starting kernel ... » 2024-09-02 18:34:18
我也遇到了相同的问题,具体情况和inia一样,
开始怀疑是nand flash的问题,所以换了很多个nand flash,但是换了还是不能解决问题,
后边偶然将f1c100s换成了f1c200s就没有这个问题,
所以怀疑解压kernel的时候内存占用过多,
猜测最后导致解压出顺坏了的vmlinux,我测试下来最大kernel的临界点在3m左右,大于了3m大概率就会出现问题
solution:
我通过将一些编译在内核内的东西编译成了ko文件来减小kernel本身的大小,问题轻松解决
后续:如果要根本解决问题,那么尝试改变kernel压缩策略
2. gzip (vmlinuz)
优点: 平衡了压缩比和解压缩内存的使用。解压缩速度较快,且内存占用相对较小。
缺点: 压缩比相对较低,内核映像较大。
内存使用: 较低。
3. lz4
优点: 解压缩速度非常快,适合在嵌入式系统中使用。占用较少的内存资源。
缺点: 压缩比不如 gzip 或 xz。
内存使用: 低。
猜测改为lz4情况会改善 ![]()
#3 Re: 全志 SOC » 关于nano pi从u-boot启动到kernal出现1秒的花屏问题的分析及解决方法 » 2024-08-15 10:10:12
在设置mem=30M后 free -m 发现内存的total size也少了2m
感觉这个应该不是最优解 ![]()
# cat /proc/iomem
01c00000-01c0002f : 1c00000.sram-controller
01c02000-01c02fff : 1c02000.dma-controller
01c05000-01c05fff : 1c05000.spi
01c0c000-01c0cfff : 1c0c000.lcd-controller
01c0f000-01c0ffff : 1c0f000.mmc
01c13000-01c133ff : usb@1c13000
01c13000-01c133ff : musb-hdrc.1.auto
01c13400-01c1340f : 1c13400.phy
01c20000-01c203ff : clock@1c20000
01c20800-01c20bff : 1c20800.pinctrl
01c23400-01c237ff : 1c23400.lradc
01c23c00-01c23fff : 1c23c00.codec
01c25000-01c2501f : serial
01c27000-01c273ff : 1c27000.i2c
01e60000-01e6ffff : 1e60000.display-backend
80000000-81ffffff : System RAM
80008000-807fffff : Kernel code
80900000-8096c34b : Kernel data
#
修改前的,看起来reserve是有的,等再找找问题
#4 Re: 全志 SOC » A33主线Linux跑起OpenGL/ES » 2024-07-20 20:31:02
NND, 终于跑起来了, 4.19.5内核外加补丁
请问是加的哪一个补丁呢?
在我这边手动insmod mali.ko后输出如下,看起来是和楼主一样是正常的,我的kernel版本是mainline 4.19.315
[ 87.506758] Allwinner sunXi mali glue initialized
[ 87.507330] Mali:
[ 87.507336] Found Mali GPU Mali-400 MP r1p1
[ 87.510612] Mali:
[ 87.510623] 2+0 PP cores initialized
[ 87.511784] Mali:
[ 87.511790] Mali device driver loaded
运行qt程序报错0x3003
root@hyiot-shp-a:~# QT_QPA_EGLFS_PHYSICAL_WIDTH=720 QT_QPA_EGLFS_PHYSICAL_HEIGHT=1440 QT_QPA_EGLFS_INTEGRATION=none ./2dpainting
EGL Error : Could not create the egl surface: error = 0x3003
Aborted
#5 Re: 全志 SOC » 全志A33 主线u-boot/Linux入坑记录 » 2024-05-24 11:11:15
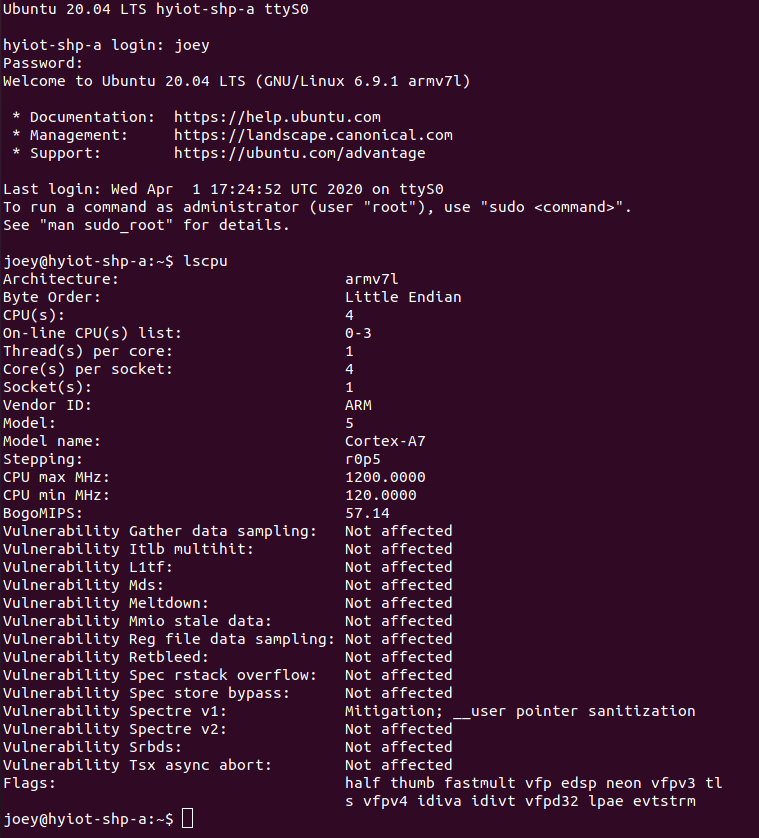
移植成功
以下是制作ubuntu20.04的rootfs的方法
Requirements
1. An x86_64 machine with Ubuntu or another Linux distribution installed.
2. `debootstrap` tool.
3. Internet connection.
4. Basic knowledge of using the terminal.
Steps to Create Ubuntu 20.04 Rootfs for ARMhf
1. Install Required Tools
First, ensure that `debootstrap` and `qemu-user-static` are installed. `qemu-user-static` allows you to run ARM binaries on your x86_64 machine.
sudo apt update
sudo apt install debootstrap qemu-user-static2. Create a Directory for the Rootfs
Create a directory where the root filesystem will be built.
mkdir -p ~/ubuntu-armhf-rootfs3. Run Debootstrap
Use `debootstrap` to create the root filesystem. Specify the architecture (`armhf`), the Ubuntu release (`focal`), and the target directory.
sudo debootstrap --arch=armhf --foreign focal ./ubuntu-armhf-rootfs https://mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn/ubuntu-ports/4. Copy QEMU Binary
Copy the `qemu-arm-static` binary into the `usr/bin` directory of the new rootfs to enable emulation.
sudo cp /usr/bin/qemu-arm-static ./ubuntu-armhf-rootfs/usr/bin/5. Chroot into the New Rootfs
Change root into the new root filesystem to complete the second stage of debootstrap.
sudo chroot ./ubuntu-armhf-rootfs6. Complete Debootstrap Second Stage
Inside the chroot environment, run the second stage of debootstrap.
/debootstrap/debootstrap --second-stage7. Configure the Rootfs
Now configure the basic settings of your new root filesystem.
- Set the hostname:
echo "ubuntu-armhf" > /etc/hostname- Set up the hosts file:
cat <<EOL > /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 ubuntu-armhf
EOL- Create fstab:
cat <<EOL > /etc/fstab
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
devpts /dev/pts devpts gid=5,mode=620 0 0
tmpfs /run tmpfs defaults 0 0
tmpfs /run/lock tmpfs nodev,nosuid,noexec 0 0
EOL- Set up networking:
cat <<EOL > /etc/network/interfaces
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
auto eth0
iface eth0 inet dhcp
EOL- Set the root password:
passwd- Create a user:
adduser ubuntu
usermod -aG sudo ubuntu- Install essential packages:
apt update
apt install sudo nano ssh8. Exit the Chroot
Exit the chroot environment.
exit9. Clean Up
Remove the `qemu-arm-static` binary from the rootfs.
sudo rm ./ubuntu-armhf-rootfs/usr/bin/qemu-arm-static10. Package the Rootfs
Finally, create a tarball of the root filesystem.
sudo tar -czvf ubuntu-20.04-armhf-rootfs.tar.gz -C ./ubuntu-armhf-rootfs .在移植完后会发现会有readonly fs的问题,其实就是挂载的时候没给rw
bootargs改为
setenv bootargs console=ttyS0,115200 earlyprintk root=/dev/mmcblk0p2 rootwait rw panic=10就一切正常了
#8 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 打造 HI3518 摄像头从入门到放弃最强帖 » 2023-09-09 17:19:37
#9 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 打造 HI3518 摄像头从入门到放弃最强帖 » 2023-09-09 17:18:05
页次: 1
- 首页
- » 搜索
- » joeydeng 发表的帖子
太原小智科技有限责任公司 - 东莞哇酷科技有限公司联合开发