- 首页
- » 搜索
- » sven1234 发表的帖子
页次: 1
#1 Re: 全志 SOC » 全志V3S移植移远EC200S » 2022-11-07 19:19:04
#2 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 咸鱼找到一个BK7252方案的Wi-Fi摄像头,跑的还是RT-Thread » 2022-11-02 17:16:13
sven1234 说:RT-Thread睿赛德自己的开发板麻雀1号就是这个平台啊。他们有全套资料。
有链接嘛?
奶牛网盘: https://realthread.cowtransfer.com/s/3f150ff46bfa49
百度网盘: https://pan.baidu.com/s/12ZpJO0Hn_D9_ZtAiXe2TQQ (提取码:6fpj)
https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a230r.1.14.1.2fd54ea1otMJIL&id=606684373403&ns=1&abbucket=5
#3 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 沁恒ch565w测试 USB3.0速度和千兆以太网速度 » 2022-09-29 11:10:42
#4 Re: Xilinx/Altera/FPGA/CPLD/Verilog » 开源一个自己画的超迷你FPGA核心板 » 2022-09-27 23:42:47
要支持AGM的移步下面帖子:
https://whycan.com/t_7284.html
#5 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 沁恒ch565w测试 USB3.0速度和千兆以太网速度 » 2022-09-27 10:15:02
#10 Re: 感芯科技 » 【代码分享】MC3172大战WS2812B » 2022-08-19 17:43:51
#12 Re: 感芯科技 » 感谢哇酷开发者社区为我们提供这个论坛板块 » 2022-07-30 00:28:06
#14 Re: 感芯科技 » MC3172用户测评汇总(持续更新) » 2022-07-28 12:43:21
#16 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 咸鱼找到一个BK7252方案的Wi-Fi摄像头,跑的还是RT-Thread » 2022-07-06 17:13:06
#18 Re: 全志 SOC » 继续再发一贴:对于GPS这种正常只需要RX,不需要TX的设备 » 2022-06-24 12:19:41
#20 Re: Xilinx/Altera/FPGA/CPLD/Verilog » 最近研究了下Xilinx 的XVC,发现jlink有了个新玩法,可以白嫖一个xilinx高速下载器了 » 2022-05-06 22:56:58
#21 Re: ST/STM8/STM8S/STM8L » stm8替换国产 » 2022-03-21 13:33:35
#22 Re: 全志 SOC » 网站需要改革,放开文件下载权限(不需要与积分挂钩) » 2022-01-13 11:26:20
#23 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 孔雀石 SDR STM32H7-SDR 验证成功 » 2020-09-09 00:58:35
#24 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 孔雀石 SDR STM32H7-SDR 验证成功 » 2020-09-09 00:52:37
上传一个MSI001的Datasheet msi001.pdf
#25 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 孔雀石 SDR STM32H7-SDR 验证成功 » 2020-09-07 14:05:31
#31 Re: DIY/综合/Arduino/写字机/3D打印机/智能小车/平衡车/四轴飞行/MQTT/物联网 » 请教大家,有没有能跑DOS系统的开发板 » 2020-05-13 21:23:52
不知道算不算挖坟了,让我想起个东西叫86Duino。x86内核,可以跑DOS。
https://item.taobao.com/item.htm?spm=a1z10.1-c-s.w4004-4394413220.2.66a93b7csnIoYg&id=35688310882
#32 Re: ESP32/ESP8266 » 分享一个自己做的wifi时钟代码 » 2020-05-13 20:41:43
#33 ESP32/ESP8266 » 分享一个自己做的wifi时钟代码 » 2020-05-13 01:04:42
- sven1234
- 回复: 12
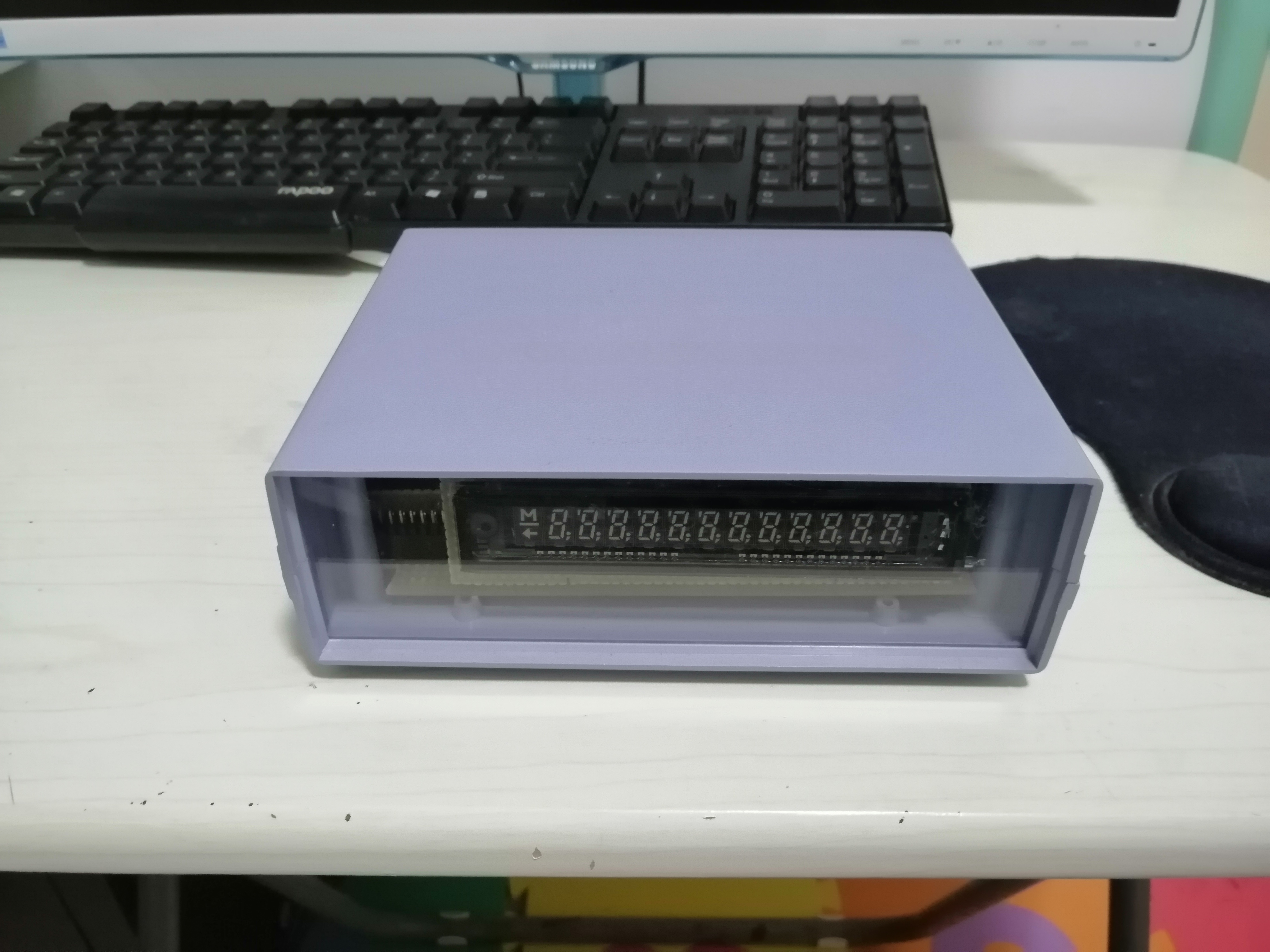
买了个VFD屏,无聊做了个时钟,但感觉用RTC自己跑时间久了总是不准,所以用ESP8266做了个NTP Client并且分解了年月日。
代码如下。写得有点粗糙见笑了。刚入坛,多见谅。
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
char ssid[] = "SSID"; // your network SSID (name)
char pass[] = "password"; // your network password
unsigned int localPort = 2390; // local port to listen for UDP packets
IPAddress timeServerIP;
const char* ntpServerName = "202.118.1.130";//"1.cn.pool.ntp.org";
const int NTP_PACKET_SIZE = 48; // NTP time stamp is in the first 48 bytes of the message
byte packetBuffer[ NTP_PACKET_SIZE]; //buffer to hold incoming and outgoing packets
WiFiUDP udp;
// send an NTP request to the time server at the given address
unsigned long sendNTPpacket(IPAddress& address)
{
Serial.println("sending NTP packet...");
// set all bytes in the buffer to 0
memset(packetBuffer, 0, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
// Initialize values needed to form NTP request
// (see URL above for details on the packets)
packetBuffer[0] = 0b11100011; // LI, Version, Mode
packetBuffer[1] = 0; // Stratum, or type of clock
packetBuffer[2] = 6; // Polling Interval
packetBuffer[3] = 0xEC; // Peer Clock Precision
// 8 bytes of zero for Root Delay & Root Dispersion
packetBuffer[12] = 49;
packetBuffer[13] = 0x4E;
packetBuffer[14] = 49;
packetBuffer[15] = 52;
// all NTP fields have been given values, now
// you can send a packet requesting a timestamp:
udp.beginPacket(address, 123); //NTP requests are to port 123
udp.write(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE);
udp.endPacket();
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println();
Serial.println();
// We start by connecting to a WiFi network
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, pass);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.println("Starting UDP");
udp.begin(localPort);
Serial.print("Local port: ");
Serial.println(udp.localPort());
}
unsigned char rmdp[12]={0,31,59,90,120,151,181,212,243,273,304,334};
unsigned char rmdr[12]={0,31,60,91,121,152,181,213,244,274,305,335};
void loop()
{
//get a random server from the pool
WiFi.hostByName(ntpServerName, timeServerIP);
sendNTPpacket(timeServerIP); // send an NTP packet to a time server
// wait to see if a reply is available
delay(1000);
int cb = udp.parsePacket();
if (!cb) {
Serial.println("no packet yet");
}
else {
Serial.print("packet received, length=");
Serial.println(cb);
// We've received a packet, read the data from it
udp.read(packetBuffer, NTP_PACKET_SIZE); // read the packet into the buffer
//the timestamp starts at byte 40 of the received packet and is four bytes,
// or two words, long. First, esxtract the two words:
unsigned long highWord = word(packetBuffer[40], packetBuffer[41]);
unsigned long lowWord = word(packetBuffer[42], packetBuffer[43]);
// combine the four bytes (two words) into a long integer
// this is NTP time (seconds since Jan 1 1900):
unsigned long secsSince1900 = highWord << 16 | lowWord;
secsSince1900=secsSince1900+28800;
Serial.print("Seconds since Jan 1 1900 = " );
Serial.println(secsSince1900);
unsigned long second=secsSince1900%60;
unsigned long minute=secsSince1900/60%60;
unsigned long hour=secsSince1900/3600%24;
unsigned long num_date=secsSince1900/86400;
unsigned long num_four_year=(num_date-365)/1461;
unsigned long last_date=(num_date-365)%1461;
unsigned long last_num_year=last_date/365;
unsigned long last_year_date=last_date-last_num_year*365;
unsigned long year=1901+num_four_year*4+last_num_year;
unsigned long month=last_year_date/30+1;
unsigned long date=0;
if(last_num_year==3){
date=last_year_date-rmdr[month-1]+1;
}else{
date=last_year_date-rmdp[month-1]+1;
}
unsigned long day=num_date%7+1;
Serial.print(year);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.print(month);
Serial.print("-");
Serial.print(date);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(day);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(hour);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.print(minute);
Serial.print(":");
Serial.println(second);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Serial.print("CMD");
Serial.write(year%100/10);Serial.write(year%10);
Serial.write(month/10);Serial.write(month%10);
Serial.write(date/10);Serial.write(date%10);
Serial.write(day);
Serial.write(hour/10);Serial.write(hour%10);
Serial.write(minute/10);Serial.write(minute%10);
Serial.write(second/10);Serial.write(second%10);
Serial.write(0x0d);Serial.write(0x0a);
}
// wait ten seconds before asking for the time again
delay(10000);
}#34 Xilinx/Altera/FPGA/CPLD/Verilog » 分享一个国产CPLD/FPGA芯片资料:AGM的AG1280Q48 » 2020-05-13 00:50:47
- sven1234
- 回复: 22
最近因为有个小项目需要一个尺寸小资源也不多的CPLD/FPGA芯片,找了很久无意中发现了这个AGM的AG1280Q48,用得感觉甚好。
特此分享点资料。
芯片价格也不贵,淘宝上零售的也就6块不到。
Feature:
LUTs:1280
Distributed RAM (Kbits):10
EBR SRAM (Kbits):68
Maximum User I/O pins:40
Number of PLLs:1
Package:48-Pin QFN
小小芯片,资源比EPM240是多不少了。
今天就先传点收集的资料了,日后再发点Demo上来。
资料如下:
377988831AG1280Q48_SCH_开发板原理图_备注说明.pdf
MANUAL_Supra_6_1.pdf
MANUAL_AG1280.pdf
C133767_AG1280Q48托盘_2017-11-13.pdf
淘宝上买的板子
放开发板链接不是发广告,我的资料都是问这个老板要的,老板人还行。但老实说这个板子设计得真是有点……
#35 Re: RISC-V » 刚收到货的 诛仙剑 C-SKY Linux 开发板 » 2020-05-11 18:12:58
页次: 1
- 首页
- » 搜索
- » sven1234 发表的帖子
太原小智科技有限责任公司 - 东莞哇酷科技有限公司联合开发