楼主 # 2022-11-25 12:44:38 分享评论
- just
- 会员
- 注册时间: 2022-06-13
- 已发帖子: 6
- 积分: 31
简单的点灯求助
本人初学linux驱动,买了个sw106的套件,正好当开发板用。
板子上有两个灯,接的PE6和PE7,想用这个来实现helloword。但遇到了问题
先说一下流程,本想用设备树,但根基都不稳,还是算了,先按传统的来,于是在本论坛找了一个代码改动了一下
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
static struct class *SW106LedClass;
//STATUS-LED:PE7
#define PIO_BASE (0x0300B000)
volatile unsigned long *PortECFG[4] = {NULL};
volatile unsigned long *PortEData = NULL;
static int SW106LedOpen(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
//configure PE7 to output mode
uint32_t lastValue = *PortECFG[0];
lastValue &= 0x1fffffff;
*PortECFG[0] &= lastValue;
printk("led opened %ld\n",*PortECFG[0]);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t SW106LedWrite(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
int val;
copy_from_user(&val, buf, count);
printk("led write %d\n",val);
if (val == 1)
*PortEData |= (1 << 7);
else
*PortEData &= ~(1 << 7);
return 0;
}
static struct file_operations SW106LedFileOp = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = SW106LedOpen,
.write = SW106LedWrite,
};
int major;
int SW106LedInit(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, "led", &SW106LedFileOp);
SW106LedClass = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "led");
device_create(SW106LedClass, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "led");
PortECFG[0] = (volatile unsigned long*)(PIO_BASE+0x24*4);
PortECFG[1] = PortECFG[0] + 4;
PortEData = (volatile unsigned long*)(PIO_BASE+0xA0);
printk("portecfg %X portedata %X\n",PortECFG[0],PortEData);
return 0;
}
static void SW106LedExit(void)
{
unregister_chrdev(major, "led");
device_destroy(SW106LedClass, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(SW106LedClass);
iounmap(PortECFG[0]);
}
module_init(SW106LedInit);
module_exit(SW106LedExit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("JustQin");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("SW GPIO USER driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");地址依据a133的用户手册
基地址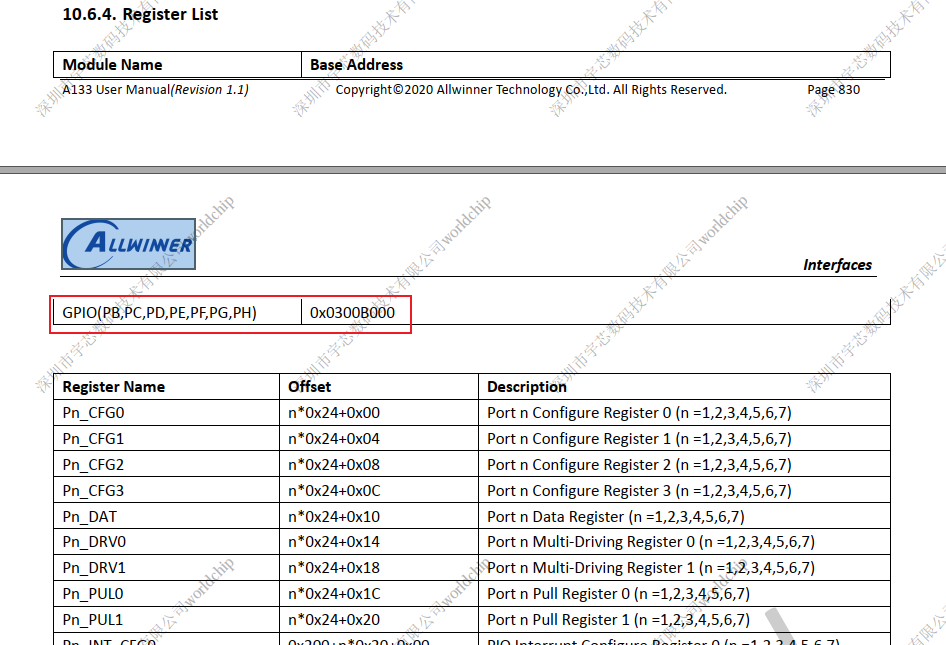
配置模式地址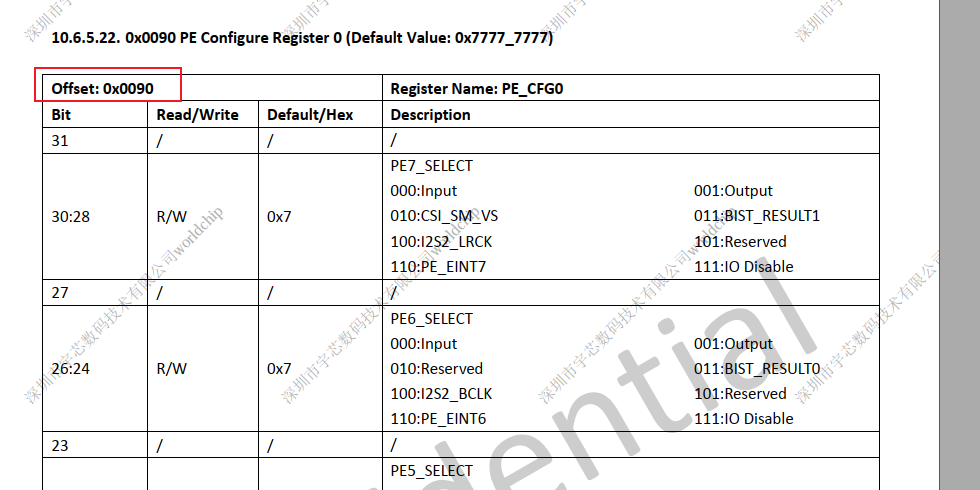
设置数据地址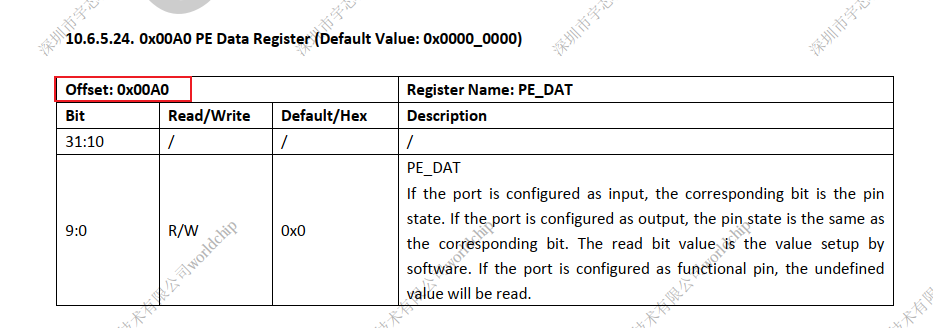
最后的结果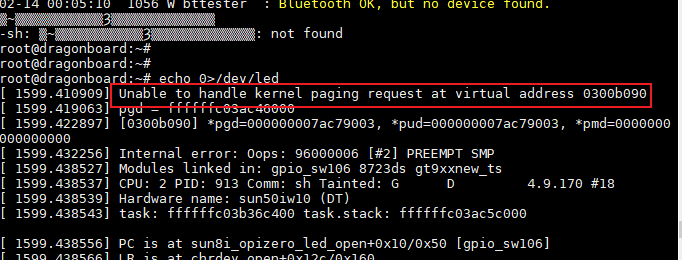
到这儿就真不知道咋回事了,哪位能帮忙指点一下吗?不胜感激
离线
楼主 #3 2022-11-25 16:34:56 分享评论
- just
- 会员
- 注册时间: 2022-06-13
- 已发帖子: 6
- 积分: 31
Re: 简单的点灯求助
海石生风 说:
学驱动动最好先仔细了解下MMU,支持进程的操作系统其内存地址都是虚拟化的即由MMU管理,故不能直接操作物理地址,要通过地址映射进行访问。
那我采用库函数来搞算了,gpio set value 那些
离线
楼主 #4 2022-11-25 16:36:16 分享评论
- just
- 会员
- 注册时间: 2022-06-13
- 已发帖子: 6
- 积分: 31
Re: 简单的点灯求助
@落日余晖
你这个方式我这边试了,是可以的,你那边我就不知道了
离线
感谢为中文互联网持续输出优质内容的各位老铁们。
QQ: 516333132, 微信(wechat): whycan_cn (哇酷网/挖坑网/填坑网) service@whycan.cn
太原小智科技有限责任公司 - 东莞哇酷科技有限公司联合开发
太原小智科技有限责任公司 - 东莞哇酷科技有限公司联合开发